Types of Diamond blades by manufacturing method
Diamond blades are catalogued by manufacturing method:
1.Electroplated diamond blade
Diamonds are electroplated onto the metal blade base. Electroplated diamond blades can be made to be very thin. The thickness of the blade can be tens of microns and can be used in precise cuttings. Actually, the Bond is Nickel.
2.Vacuum Brazed diamond blade
Synthetic diamond particles are welded to the outside edge of the circular saw blade via a vacuum brazing furnace. All of the diamond particles are on the exterior cutting edge of the blade, with no metal/diamond mixture. When using a vacuum brazed diamond blade you need not match the type of blade with the material being cut. Depending on the manufacturers recommended blade application, vacuum brazed blades will cut a wide variety of material ranging from concrete to masonry, materials like stone and brick, to steel, various irons, even plastic, tile, wood & glass. Always consult your blade manufacturer for a full list of cutting applications.
Smaller finer synthetic diamond grits will provide a smoother finish with no chipping on tile or burring on steel. Larger diamond grits will provide a faster cutting speed, but will likely cause chipping, burring or cracking of your material. Fire departments require blades to be made with a very large diamond grit, to tear through material fast, while a happy medium is required for the production industry.
3.Sintered Metal-bonded diamond blade
Sintered metal-bonded diamond blades are the most common type. A blade of this type is composed of a Steel core (the blade's base is steel plate, unlike diamond wire and diamond segments which are made by combining synthetic diamond crystals with powder and then sintering them. The diamond segments are also known as the "cutting teeth" of the blade.
The steel core can vary in design. Some of them have spaces (known as gullets) between each segment to provide cooling and slurry removal, while others have a single continuous rim for smoother chip-free cutting. The type of core that can be used depends on the type of materials that the diamond blade is designed to cut.
Generally, there are three types of sintered metal-bonded diamond blades according to their manufacturing methods: wholly sintered diamond blades(cold pressed or hot pressed), silver brazed diamond blades and laser welded diamond blades.
A wholly sintered diamond blade is made by putting the steel core together with the diamonds and the metal bond materials into a mold and then sintering them in a sintering machine. So the diameter of wholly sintered diamond blades is not very big and normally is not bigger than 400 millimetres (16 in). Also because its participating in the sintering process, the steel core cannot be quenched, so the hardness and strength of the core is not very high, these types of diamond blades may deform in high-load and high-intensity cutting processes. Therefore, in some cases wholly sinter diamond blades' cutting efficiency cannot be very high.
Silver brazed diamond blades and laser welded diamond blades, however, do not have this problem. Because their diamond segments and steel core are treated separately. The steel core can be quenched and processed with other heat treatments, so its hardness and strength can be high, therefore the blade can be used in high-load and high-intensity cutting processes without deformation and high cutting efficiency can be gained.
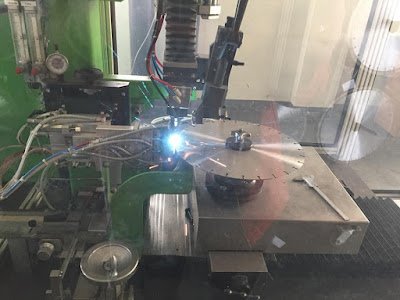
Silver brazed diamond blades' diamond segments are brazed to the steel core using a silver solder. Silver brazed diamond blades can only be used in wet cuttings. Because if they are used in dry cuttings, the silver solder may melt under the high temperature generated in the dry cutting and the segments can break from the steel core and be extremely dangerous. While the laser melts and combines the metal of the diamond segment and the steel core creating a stronger weld, which can hold the segments even in high temperatures, so laser welded diamond blades can be used to cut many types of stone without water cooling. However, when cutting very hard or abrasive materials, e.g., concrete containing reinforcing rebar, laser welded diamond blades should also be used with adequate water. Otherwise, it is fairly possible that the diamond segment itself breaks or the steel core below the segment wears and breaks, and then causes serious security issues.
1.Electroplated diamond blade
Diamonds are electroplated onto the metal blade base. Electroplated diamond blades can be made to be very thin. The thickness of the blade can be tens of microns and can be used in precise cuttings. Actually, the Bond is Nickel.
2.Vacuum Brazed diamond blade
Synthetic diamond particles are welded to the outside edge of the circular saw blade via a vacuum brazing furnace. All of the diamond particles are on the exterior cutting edge of the blade, with no metal/diamond mixture. When using a vacuum brazed diamond blade you need not match the type of blade with the material being cut. Depending on the manufacturers recommended blade application, vacuum brazed blades will cut a wide variety of material ranging from concrete to masonry, materials like stone and brick, to steel, various irons, even plastic, tile, wood & glass. Always consult your blade manufacturer for a full list of cutting applications.
Smaller finer synthetic diamond grits will provide a smoother finish with no chipping on tile or burring on steel. Larger diamond grits will provide a faster cutting speed, but will likely cause chipping, burring or cracking of your material. Fire departments require blades to be made with a very large diamond grit, to tear through material fast, while a happy medium is required for the production industry.
3.Sintered Metal-bonded diamond blade
Sintered metal-bonded diamond blades are the most common type. A blade of this type is composed of a Steel core (the blade's base is steel plate, unlike diamond wire and diamond segments which are made by combining synthetic diamond crystals with powder and then sintering them. The diamond segments are also known as the "cutting teeth" of the blade.
The steel core can vary in design. Some of them have spaces (known as gullets) between each segment to provide cooling and slurry removal, while others have a single continuous rim for smoother chip-free cutting. The type of core that can be used depends on the type of materials that the diamond blade is designed to cut.
Generally, there are three types of sintered metal-bonded diamond blades according to their manufacturing methods: wholly sintered diamond blades(cold pressed or hot pressed), silver brazed diamond blades and laser welded diamond blades.
A wholly sintered diamond blade is made by putting the steel core together with the diamonds and the metal bond materials into a mold and then sintering them in a sintering machine. So the diameter of wholly sintered diamond blades is not very big and normally is not bigger than 400 millimetres (16 in). Also because its participating in the sintering process, the steel core cannot be quenched, so the hardness and strength of the core is not very high, these types of diamond blades may deform in high-load and high-intensity cutting processes. Therefore, in some cases wholly sinter diamond blades' cutting efficiency cannot be very high.
Silver brazed diamond blades and laser welded diamond blades, however, do not have this problem. Because their diamond segments and steel core are treated separately. The steel core can be quenched and processed with other heat treatments, so its hardness and strength can be high, therefore the blade can be used in high-load and high-intensity cutting processes without deformation and high cutting efficiency can be gained.
Silver brazed diamond blades' diamond segments are brazed to the steel core using a silver solder. Silver brazed diamond blades can only be used in wet cuttings. Because if they are used in dry cuttings, the silver solder may melt under the high temperature generated in the dry cutting and the segments can break from the steel core and be extremely dangerous. While the laser melts and combines the metal of the diamond segment and the steel core creating a stronger weld, which can hold the segments even in high temperatures, so laser welded diamond blades can be used to cut many types of stone without water cooling. However, when cutting very hard or abrasive materials, e.g., concrete containing reinforcing rebar, laser welded diamond blades should also be used with adequate water. Otherwise, it is fairly possible that the diamond segment itself breaks or the steel core below the segment wears and breaks, and then causes serious security issues.
 |
| laser welded diamond bladelaser welded diamond blade |
.jpg)
.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment
Please make some comments on them. Thanks!!!